What Is Sciatica?
Sciatic pain can be excruciating, including symptoms of shooting pain into the buttocks and back of leg, usually on one side of the body, numbness, tingling and/or weakness. The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve trunk in the body originating from L4 – S2 spinal segments; when it leaves the pelvis it enters the gluteal region where it sits under the piriformis muscle and continues between the hamstring muscles to the back of the knee where it then branches into the tibial and peroneal nerves.
The most common cause of sciatic symptoms is due to a lumber disc bulge or herniation, causing direct compression or chemical irritation to the nerve root; although there are other causes such as spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal), degeneration which may lead to osteophytes (bone spurs), or piriformis syndrome where the sciatic nerve is irritated or compressed by the piriformis muscle.
What Causes A Disc Bulge?
The intervertebral discs between our vertebrae are made up of two components; a harder outer layer called the annulus fibrosus which surrounds the softer gel-like core which is the nucleus pulposus. The role that intervertebral discs’ play is as a shock absorber for the spine and to protect the nerves that run down the middle of our spines.
Injury to the annulus fibrosus can lead to the nucleus pressing outwards on the disc wall, leading to either chemical irritation and inflammation around the nerve root, or compression of the nerve root as it exits the spine.
There are multiple causes for a disc bulge, herniation or disc rupture to occur:
- Repetitive Microtrauma
A common reason is prolonged poor sitting, standing, or working posture. Prolonged or sustained slouching or forward bending of the spine causes pressure and weakening of the annulus fibrosus and the nucleus will push out through a tear in the outer layer. Also at risk are people with jobs that require repetitive heavy lifting, pushing, pulling and twisting.
- Genetic Factors
Some people inherit a predisposition to spinal disc injuries. Research has found that some collagen genes impair the ability for collagens to interact with each other, which leads to degeneration and instability of the disc.
- Trauma
Sudden unexpected load as in the case of motor vehicle accident, poor lifting technique or heavy load at the gym, can cause a sudden tearing of the annulus fibres
- Environmental Factors
Other factors such as excess weight, reduced core strength, decreased lower limb strength may all have an impact on the lumbar spine as this affects correct spinal alignment increasing the risk of disc degeneration. Also smoking reduces the oxygen flow to the spinal disc, therefore causing increased risk of degeneration.
What Is The Difference Between Disc Bulge And Herniation?
A disc bulge (commonly known as slipped disc) means that the nucleus has not pushed through the outer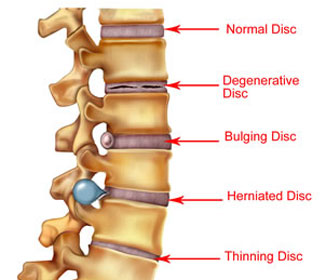 layer of the disc. When symptomatic it has bulged enough to put pressure on the nerve root, or cause chemical irritation due to inflammation. A disc bulge in many cases may not be symptomatic and is often considered to be a normal part of ageing; however, a disc bulge may be a precursor to disc herniation if not properly rehabilitated. A disc herniation refers to when the nucleus has pushed through a tear in the outer layer of the disc.
layer of the disc. When symptomatic it has bulged enough to put pressure on the nerve root, or cause chemical irritation due to inflammation. A disc bulge in many cases may not be symptomatic and is often considered to be a normal part of ageing; however, a disc bulge may be a precursor to disc herniation if not properly rehabilitated. A disc herniation refers to when the nucleus has pushed through a tear in the outer layer of the disc.
A disc bulge is usually aggravated by activities including sitting, forward bending, lifting, coughing and sneezing and may refer pain to the knee, and sometimes to the ankle. Symptoms such as numbness or weakness in the leg may indicate a more severe disc injury. Numbness of the groin, and partial, intermittent or significant loss of bladder and bowel function must seek prompt medical attention as this indicates more severe injury to the cauda equina and is a medical emergency.
How Is A Bulging Disc Diagnosed?
A disc bulge can usually be diagnosed through a series of special tests in clinic and your therapist will commence a disc rehabilitation program immediately. In most cases symptoms will start to ease within the first but up to three treatments. If no significant changes are noted within three treatments, then further diagnostic scanning such as MRI or CT scan may be required, as this is the most accurate way of assessing the extent of your spinal disc injury.
Kelly has trained in the McKenzie Method for the treatment and rehabilitation of lumbar spine disc injuries. Treatment of low back pain using this method is proving to be successful both in clinic and via Telehealth consultation. If you would like to know more about this treatment and rehabilitation technique please contact Kelly on 0401 492 832 or BOOK ONLINE